Integrate, accept, and manage payments - all in a single platform.
Our merchant processing solution empowers businesses with a user-friendly portal that creates a seamless experience from 'process' to 'paid'.
This comprehensive credit card processing platform also features numerous integrations and add-ons that boost its functionality and allows users to offer even greater convenience to customers.
Fulfill all your payment needs... and then some.
The CardPointe platform and devices include additional features that make accepting and managing payments as effortless as possible.
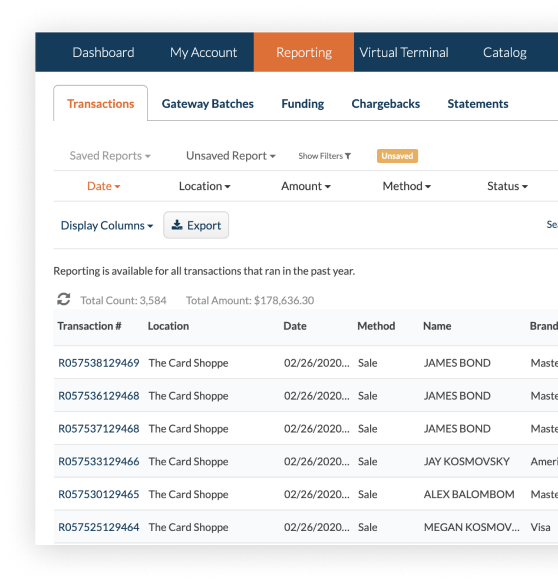
Transaction Management
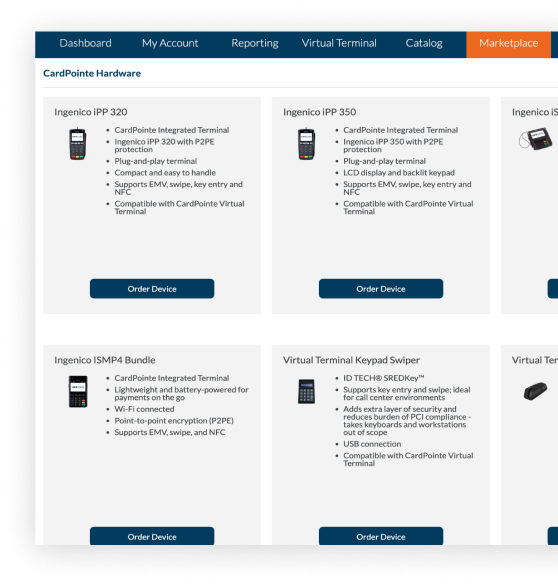
CardPointe Terminal
Plug-and-play terminal for swipe, dip, and tap transactions protected by point-to-point encryption (P2PE)
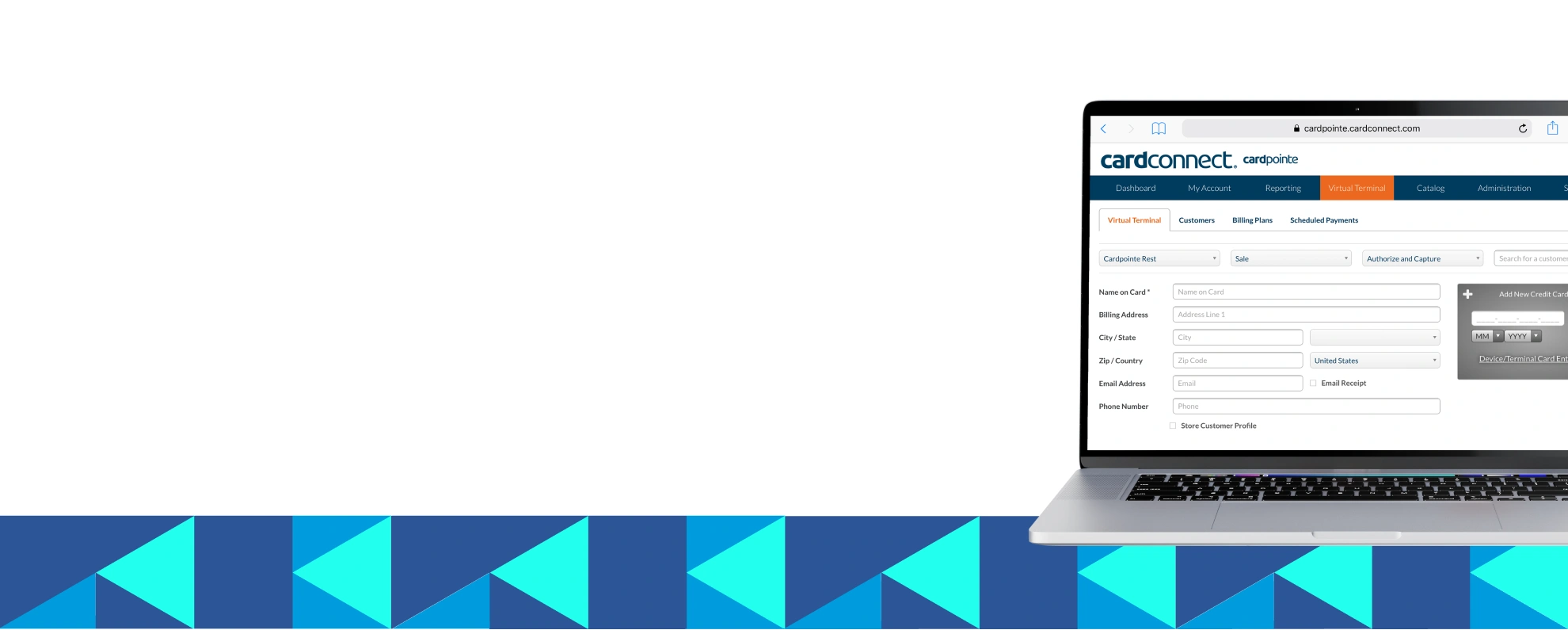
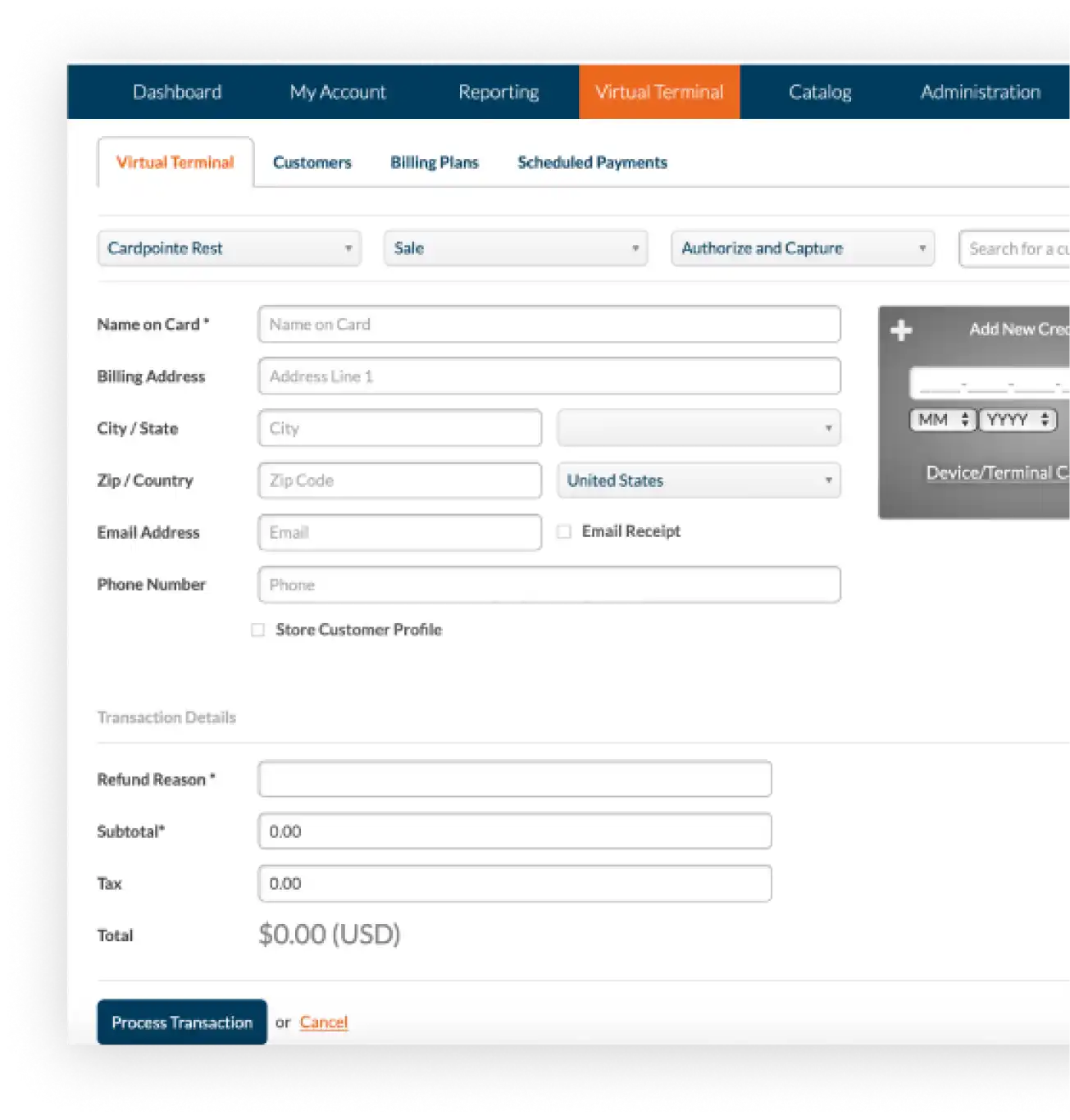
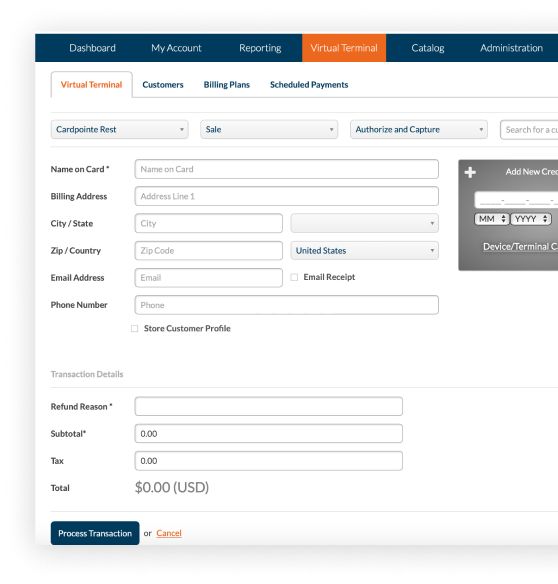
Virtual Terminal
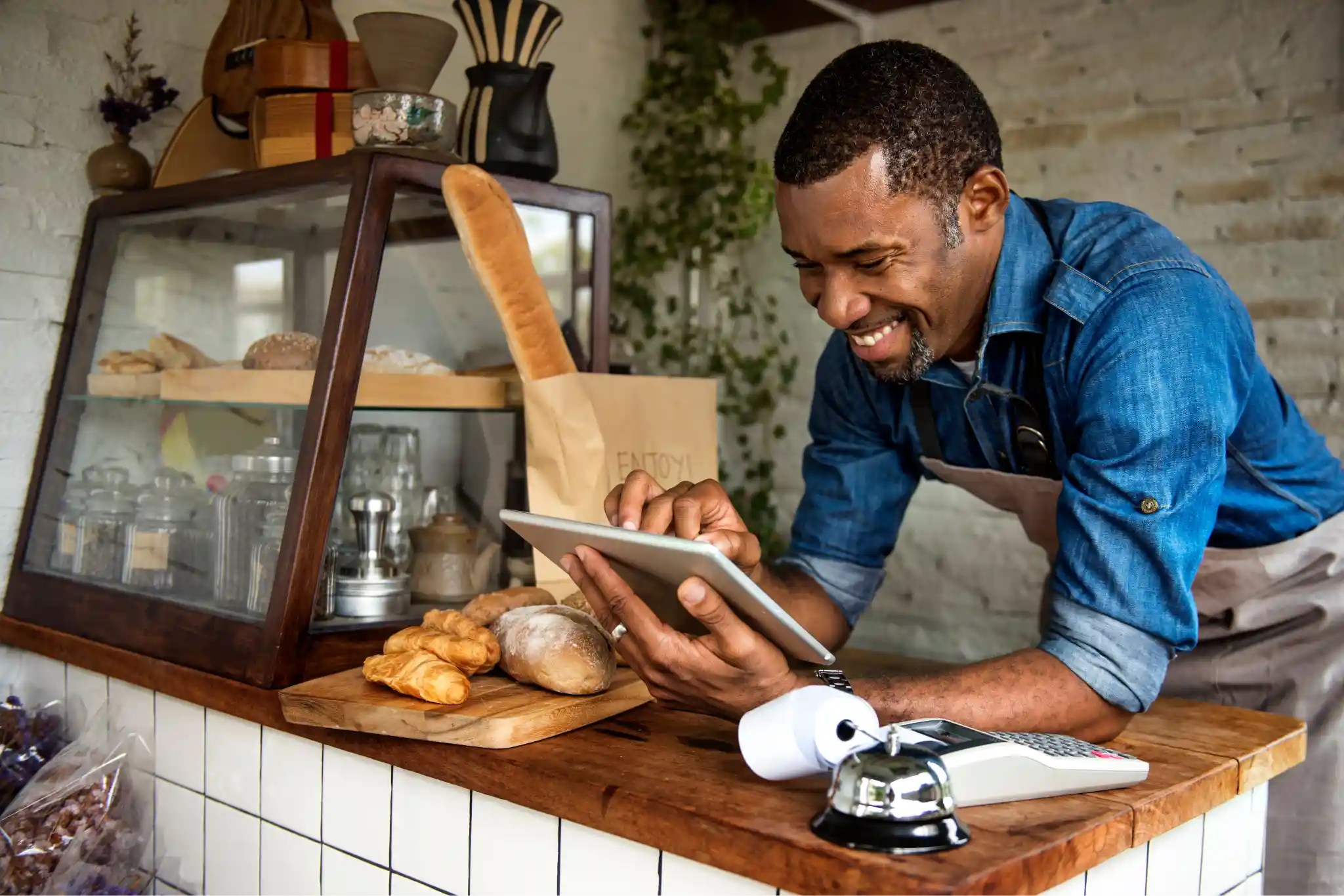
Mobile App + Device
Integrations + Add-ons
Got questions? We got answers.
Contact Us
Your success in payments starts here! Please select your partnership type below so we can connect.